SETTLEMENTS & URBAN MORPHOLOGY







Settlement – a place where people live
-
Dispersed settlements
-
Temporary camps of hunters/herders
-
Permanent settlements
-
Large urban agglomerations
Conurbation/ metropolitan Area – A super-city consisting of multiple cities and towns;
Population is usually several million
Large city – A city with a large population (1 million ppl) and many services
provided
City – Having abundant services, population of over 100, 000 people
Large town – A population of 20,000 to 100, 000; urban area with a particular
administration/legal/historical status
Town – a population of 1000 to 20,000 people
Village – Generally doesn’t have many services, population of 100 to 1000; clustered human settlements/community
Hamlet – Tiny population (> 100) and very few services and buildings
Isolated Dwelling – Only 1-2 buildings or families, negligible services
***A conurbation is an urban area comprising of a number of metropolitan areas that are connected with one another and are usually interdependent with one another economically and socially. Merged after continual population growth and physical expansion to form a continuous urban and industrially developed area
Site – Actual piece of ground on which settlement is built; the settlement’s exact location
SITE FACTORS:
-
Water Supply – Clean supply of water for consumption and domestic usage
-
Relief – Area needs to be high enough to be safe from flooding, low enough to be sheltered from strong winds
-
Defense – Protection from attackers (natural e.g. hilltop, inside of a river meander)
-
Transport – A site at crossroads, rivers or coast gives easier access to other settlements
-
Soil – Deep fertile soil made farming and animal rearing easier
-
Resources – Sources required for building, heating, fuel etcetera (timber, rock wood)
Situation – Refers to location of the settlement in relation to surrounding areas
*If a settlement has food access to natural resources and other settlements, it grows in size. Many settlements with a good site and situation have grown into large cities.
EXAMPLE CITY – PARIS
-
Capital of France, largest city in Europe, population of 10 million
-
Began in 3 BC
-
Sited on a small island in river Siene
-
Site good for defense and a good crossing point across the river
-
Fertile soil of Siene was excellent for farming
-
Under Roman rule, Paris grew and became the center of a network of roads across Europe
-
Center of many international air routes, railways and roads (based on site)
Settlement Patterns
Dispersed – Far apart from each other
Linear – Long and narrow settlements
Nucleated – Clustered settlements
*Dispersed settlements are usually farms (field land) or in
mountainous regions (hard to live in areas)
*Linear settlements follow feature of land (roads, shape,
railways, rivers etc.)
*Buildings clustered around a central point (crossroad,
church, water supply, market etc.) in a nucleated settlement
*Planned settlements have a regular pattern
City Layout – The easy a city’s streets and buildings are distributed
TYPES:
-
Irregular: Unplanned urban growth, no particular order, narrow and winding streets, few open spaces (medieval/Muslim towns)
-
Grid Plan: Streets run at right angles to each other, typical of North American cities
-
Radio-centric: Streets radiate out from a central point
FUNCTIONS OF A SETTLEMENT
***Activities that take place inside a settlement
-
Farming
-
Markets and inns
-
Industrial
-
Residential
-
Administrative
-
Commercial
-
Services (schools, libraries, hospitals)
-
Tourism
Problems of Urban Growth
-
Housing – Lack of housing, affordability of proper housing; leads to development of squatter settlements
-
-
Provide high rise flats (e.g. Singapore & Hong Kong)
-
Low cost housing to relocate slum dwellers
-
Improve living conditions of squatter settlements (piped water and sanitation)
-
Reduce rural-urban migration by improving rural services/opportunities
-
-
-
Water Supply – Shortage of water and poor piping system
-
-
Build water reservoirs
-
More treatment plants, remove and replace deteriorating pipes
-
Awareness of water conservation
-
-
-
Transport – Too many cars, poor public transport system
-
-
Extensive framework of roads and railways
-
Build expressways and wider roads for traffic flow
-
Encourage and develop public transport
-
-
-
Pollution – Domestic and industrial waste contribution to land pollution
-
-
Impose heavy fines
-
Collect waste 3x a day
-
Increase sewage pipelines
-
Piling work to be done in daylight
-
More tree plantation
-
Awareness of health, hygiene and pollution
-
-
Rural settlements are changing in both LEDCs and MEDCs due to the following:
-
Migration (rural -> urban & urban -> rural)
-
Urban growth
-
Technological change
-
Rural planning policies
-
Government finding
CHANGES IN RURAL AREAS IN LEDCs
CHANGES IN RURAL AREAS OF MEDCs
*Rural population has changed in character (gentrification)
Counter urbanization
-
The economy is no longer dominated by agriculture and employment in agriculture
(mechanized farming)
-
Farm diversification (changing use of area)
-
Higher house prices and lack of affordable housing
-
Formation of metropolitan villages
-
Rural depopulation
-
Decline of rural services and public transport (everyone has cars)
Urbanization – The growth in the population of people living in towns or cities.
-
Urban regeneration: Improve an urban area in decline with a mix of urban redevelopment and renewal
-
Urban redevelopment: complete change of existing site infrastructure/buildings and construction of new buildings from scratch
-
Urban renewal: Keeping best elements of existing urban environments and adapting them to new usage
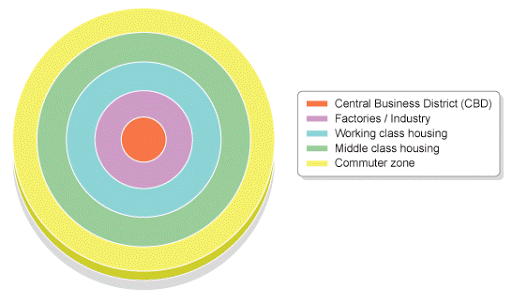
1 – BURGESS – CONCENTRIC ZONE MODEL
2 – HOYT – SECTOR MODEL
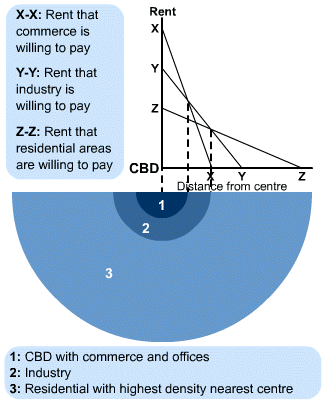
3 – ALONSO’s THEORY OF BIDRENT
***Land expensive towards center, so high, middle, low respectively
Benefits of Urbanization
-
Economic Growth
-
Social mobilization
-
Empowerment of women
-
Greater access to education and health services (contraceptives!)
-
Helps decrease population growth
-
Enormous opportunity for sustainable urban living in Africa and Asia
Disadvantages of Urbanization
-
Increasing separation of wealthy and poor
-
Urban sprawl results in inefficient usage of land and slum development
-
Risky and unhealthy living conditions in slums (pollution!)
-
Increase in slum dwellers (1990 – 650 million to 2012 – 863 million)
-
Global urbanization is an inevitable trend, slum growth due to bad decisions
-
Violence & unemployment
-
Pressure on resources and infrastructure
***Favelas in Rio Olympics
***Most cities are built around coastal areas (trade and transport) and are more susceptible to climate change, yet more rural-urban migration
TOP 10 ISSUES CITIES FACE/ MUST OVERCOME
-
Economic Development
-
Infrastructure
-
Public Safety
-
Budgets
-
Education
-
Housing
-
Data technology
-
Environment/energy
-
Demographics
-
Healthcare
Brownfield site – Derelict or underused industrial building and land that have potential for re-development
Counter-urbanization – A process involving the movement of population away from urban areas to a new town/estate/village
Re-urbanization – The development of activities to increase population densities within the existing built-up area of a city; may include redevelopment of brownfield sites or new business enterprises
Suburb – A residential area within or outside the boundaries of a city
Suburbanization – The outward growth of towns and cities to villages and rural areas
Urban sprawl – Uncontrolled and unplanned physical expansion of an urban area into countryside
Residential segregation – The physical separation of population by culture, income, or other criteria
Poverty
Absolute Poverty – Measures poverty in relation to the amount of money necessary to meet basic needs such as food, clothing, and shelter (not concerned with quality of life issues or inequality in society)
Relative Poverty – In relation to the economic status of other members of the society, people are poor of they fall below prevailing standards of living in a given societal context
-
-
Lack of basic capability to function
-
Lack of provision by a community of the basic social services required
-
An income below the country’s poverty line
-
-
HOUSING POOR
-
HEALTH POOR
-
TIME POOR
Sustainable Development Goals (Created in 2016 to be done by 2030)
1. NO POVERTY
2. ZERO HUNGER
6. CLEAN WATER AND SANITATION
8. DECENT WORK AND ECONOMIC GROWTH
Causes of Poverty
-
Lack of education
-
Lack of resources
-
History
-
War and political instability
-
National debt
-
Discrimination and social inequality
-
Vulnerability to natural disasters
-
Dysfunctional families and bad parenting
How to Fight Poverty
-
The affected need to be willing to change
-
Issues must be identified
-
Be aware, generate awareness
-
Donate and volunteer
-
Create jobs
-
Raise minimum wage
-
Resource and services accessible to citizens
-
Pay equity
-
Education
-
Medical insurance
-
Reform criminal justice system
-
Self-help programs and projects
TYPES OF WASTE
-
Liquid
-
Solid
-
Organic
-
Recyclable
-
Hazardous
Waste Management
-
Landfill (Burying waste in land, developing countries)
-
Incineration/Combustion
-
Recovery and Recycling
-
Plasma Gasification (convert trash to renewable energy)
-
Composting (organic material to fertilizer)
-
Waste to energy (heating and other purposes)
-
Avoidance/waste minimization
-
Disposal in ocean/sea

