SEPARATION & PURIFICATION
Pure substance - Made up of one single element or compound.
Mixture - Made up of two or more substances that are not chemically combined.
TYPES OF SEPARATION:
1. Solid from a liquid
2. Solid from solid
3. Liquid from a solution
4. Liquid from liquid


Figure 2. Evaporation to Dryness
Solid from a Liquid
FILTRATION
- Separate insoluble solid particles from a liquid
- Residue & Filtrate
EVAPORATION TO DRYNESS
- To obtain a soluble solid from a solution by heating to dryness
- E.g. obtaining salt from sea water
CRYSTALLIZATION
- Obtain a pure solid sample from its solution
- Water is removed by heating until a saturated solution is formed.
- Saturated solution: When the maximum amount of solute is dissolved in the liquid
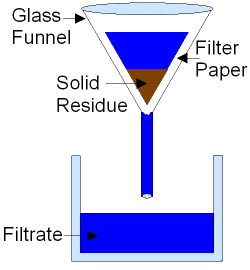
Figure 1. Filtration
Figure 3. Process of Crystallization
Figure 4. Magnetic Separation

Solids from Solids
Solution: Solvent + Solute
Solvent is higher in quantity than solute, used to dissolve the solute.
SUBLIMATION
- Used to separate a solid that sublimes (goes directly from solid to gas) from one which does not.
MAGNETIC SEPARATION
- To separate a magnetic substance from a non-magnetic substance.

Figure 5. Magnetic Separation
Liquid from Solid
SIMPLE DISTILLATION
- Pure solvent is distilled over from a solution
- Solution is heated
- At a certain temperature, the liquid starts boiling and turns to vapor. The solid is left behind whereas, the liquid is distilled through the cooling tube, and collected in a beaker.

EFFECT OF IMPURITIES ON PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS
- Lower melting point
- Increase boiling point
- Melting and boiling takes place over a range of different temperatures.

Figure 5. Simple Distillation
Liquid from Liquid
SEPARATING FUNNEL
- Used to separate immiscible liquids
- Miscible liquids dissolve in each other
- Immiscible liquids don't dissolve in each other
FRACTIONAL DISTILLATION
- Used to separate a mixture of miscible liquids with different boiling points
- Obtain nitrogen, argon and oxygen from air through this process
- Separate petroleum into useful fractions (IMPORTANT)
Figure 6. Separating funnel

Figure 7. Fractional Distillation
*Pure solids have fixed melting points (constant)
*Pure liquids have fixed boiling points (constant)
Chromatography
- Method of separating two or more components that dissolve in the same solvent
- Separate amino acids mixture
- Identify components in a sample
- Identify substance
- To check if substance is pure
Rf Value = Distance traveled by substance / distance traveled by solvent

Figure 8. Chromatography
All separation techniques can be found discussed in much greater detail in the O Level Book Chemistry Matters.