REDOX REACTIONS
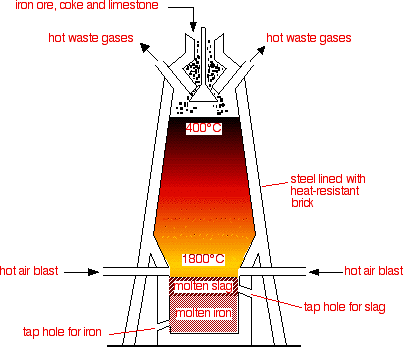
EXTRACTION OF IRON

Figure 1. Extraction of iron in blast furnace
REDOX REACTIONS - A chemical reaction in which reduction and oxidation occur simultaneously.
Reduction
Oxidation
Oxidation State - The change an atom of an element would have if it existed as an ion in a compound. Refers to the loss, gain, or share of electrons. Charge of element, but sign comes before number (e.g. Na1+ --> Na+1)
OXIDATION
REDUCTION
Hydrogen
Loss
Gain
Oxygen
Loss
Gain
Electrons
Loss
Gain
Oxidation State
Increase in state
Decrease in state
***For Hydrogen and electrons --> OIL RIG (Oxidation is loss, Reduction is gain)
Oxidation Number Rules
1. ELEMENTS BY THEMSELVES ARE 0. (ELEMENTAL/UNCOMBINED FORM e.g. Mg)
2. THE OXIDATION OF SIMPLE IONS (Na1+, Mg2+) IS THE CHARGE WITH THE SIGN IN FRONT (e.g. Na1+ --> Na+1, Mg2+ --> Mg+2)
3. OXIDATION NUMBERS IN A NEUTRAL COMPOUND MUST ADD UP TO 0.

Displacement Reaction
OXIDIZING AGENT - Always undergoes reduction itself, oxidizes something
REDUCING AGENT - Always undergoes oxidation itself, reduces something
Metals are reducing agents (get oxidized)
Non-metals are oxidizing agents (get reduced)



Reactivity Series
Most to Least Reactive
-
Potassium - K
-
Sodium - Na
-
Calcium - Ca
-
Magnesium - Mg
-
Aluminum - Al
-
Zinc- Zn (carbon only)
-
Iron - Fe
-
Lead - Pb
-
Hydrogen - H
-
Copper - Cu
-
Mercury - Hg
-
Silver - Ag
-
Gold - Au
-
Platinum - Pt
ELECTROLYSIS
HYDROGEN OR CARBON FOR REDUCTION
VERY UNSTABLE, HEAT TO DECOMPOSE
Disproportionation - Same substance is both oxidized and reduced. E.g.

Extracting Metals from Ores
Metals exist in these forms in ores:
-
Oxides
-
Hydroxides
-
Carbonates
-
Sulphates
Metals can be extracted from their ores through either electrolysis or reduction (using a reducing agent).

EXTRACTING ZINC FROM ITS ORE

CONTACT PROCESS
EXTRACTING COPPER FROM ITS ORE


ANOX REDCAT
ANOX = Anode oxidation
REDCAT = Reduction cathode
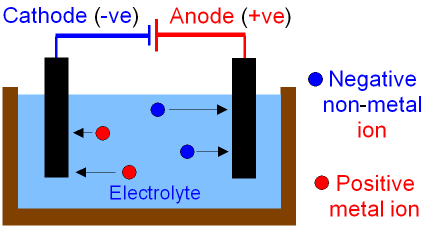
Electrolysis
Voltage Cell - Converts chemical to electrical energy
Electrolytic Cell - Converts electrical energy to chemical energy
Electrolysis - A process used to decompose a compound using current.
-
molten state (free ions)
-
aqueous state (free ions)
Can be used for extracting aluminum from its ore.
In electrolysis:
- Conductor does not get decomposed
- Electrolyte gets decomposed
Ions become discharged at electrodes.
Cathode (-)
- Positively charged ions move to negatively charged electrode.
- Ions gain electrons at the cathode
- Reduction always happens at the cathode
Anode (+)
- Negatively charged ions move to positively charged electrode.
- Ions lose electrons at the anode
- Oxidation always happens at the anode
Electrodes
-
Inert - Do not react with products of electrolysis or the electrolyte
-
Active - React with products of electrolysis or the electrolyte
Deposits of metal on electrode are silvery grey color
Gases are greenish or colorless
Electroplating / Galvonising - Process of depositing a layer of metal on another substance using electrolysis.
SELECTIVE DISCHARGE OF IONS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION
Anions

Ease of discharge increases
Figure 2. Electrolysis


Cations
-
K+ Potassium ion
-
Na+ Sodium ion
-
Ca2+ Calcium ion
-
Mg2+ Magnesium ion
-
Zn2+ Zinc ion
-
Fe2+ Iron ion
-
Pb2+ Lead ion
-
H+ Hydrogen ion
-
Cu2+ Copper ion
-
Ag+ Silver ion
Ease of discharge increases