ELECTROMAGNETIC
SPECTRUM

Electromagnetic waves - transverse waves which have the capacity to carry energy and travel without a medium (or in a vacuum)
Electromagnetic spectrum - the term used by scientist to describe the entire range of light
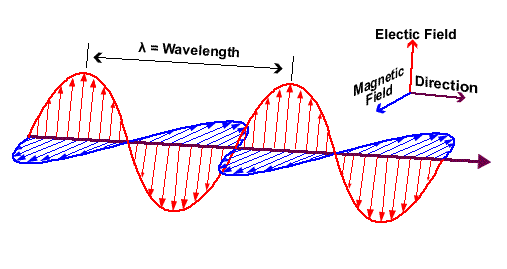
Electromagnetic waves are produced by the movement of charged particles which create an electric field and accelerate in an oscillating motion. Although their frequencies and wavelengths may differ, all electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light. EM waves have electric and magnetic fields that oscillate perpendicular to one another.
The electromagnetic spectrum exists in a large range of frequencies, spanning wavelengths from 10 picometres (10-12) to 100 kilometers.
RADIO WAVES
Radio waves have the longest wavelengths on the EM spectrum, and thus the lowest frequencies/energy.
-
Wavelength: 1mm - 100km
-
Frequency: 30 Hz - 300 GHz
-
Natural sources: lightning, other astronomical objects
-
Usage: mobiles, radio communication, broadcasting, radar

MICROWAVES
Microwaves are generally considered to overlap with the larger frequencies on the EM spectrum.
-
Wavelength: 1m - 1mm
-
Frequency: 300 MHz - 300 GHz
-
Natural sources: the sun, big bang
-
Usages: cordless phones, television broadcasts, radio astronomy, remote sensing, microwave ovens, satellite communication, LANs (usage depends on frequency)
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation permeates all of space, and was one of the key discoveries in understanding and theorizing the big bang.


INFRARED WAVES
Infrared radiation is radiation with longer wavelengths than visible light, extending from the red edge of visible light (thus given its name infrared). Infrared is known as “heat radiation”, and accounts for 49% of the sun’s heat on Earth, although all waves can heat surfaces that will absorb them.
-
Wavelength: 780nm - 1mm
-
Frequency: 300 GHz - 400 THz
-
Natural sources: the sun, any object with temperature
-
Usages: heating, communication, art analysis

VISIBLE LIGHT WAVES
Visible light is the range of wavelengths in the EM spectrum that can be detected by the human eye. Red light has the lowest frequency and greatest wavelengths, and violet light has the highest frequency and smallest wavelength.
-
Wavelength: 400nm - 700nm
-
Frequency: 430 THz - 730 THz
-
Natural sources: the sun, luminous celestial bodies
-
Usages: photography, illumination, fiber optics communication

ULTRAVIOLET LIGHT WAVES
UV light can cause chemical reactions, such as providing substances the ability to glow or fluoresce. Most UV radiation is non-ionizing, although higher energy UV radiation can occasionally be ionizing. Ionizing UV radiation is blocked by oxygen molecules in the atmosphere, meaning astronomical UV radiation does not touch the Earth’s surface.
Overexposure to UV radiation from sunlight can cause tanning, skin cancer, and other chronic health effects on the skin, eyes, and immune system. This being said, UV radiation also produces the production of vitamin D in the skin, and a large amount of positive health effects can result from this.
-
Wavelength: 10nm - 400nm
-
Frequency: 30 PHz - 750 THz
-
Natural sources: the sun
-
Usages: fluorescence, disinfection, tanning, industrial processes

X-RAY WAVES
X-ray photons carry enough energy to ionize atoms and disrupt molecular bonds. This means that exposure to x-rays for a significant period of time can cause illness and cancer-like disease within living organisms, primarily animals (including humans).
-
Wavelength: 0.01nm - 10nm
-
Frequency: 30 EHz - 30 PHz
-
Natural sources: radionuclides, cosmic rays
-
Usages: medical diagnostics, airport luggage scanners, art analysis, cancer treatment
In medical practices, the use of x-rays for imaging greatly out-values the potential radiation-based consequences that exposure can have. In diagnostic applications, low energy x-rays are absorbed by the bones in the body, allowing for an image to be formed.

GAMMA WAVES
Gamma rays are the highest energy waves on the EM spectrum. Gamma rays have high ionizing energy, and are thus biologically hazardous.
-
Wavelength: 100 pm or less
-
Frequency: 3 EHz or more
-
Natural sources: neutron stars, pulsars, supernovae, nuclear reactions
-
Usages: food irradiation, cancer therapy
